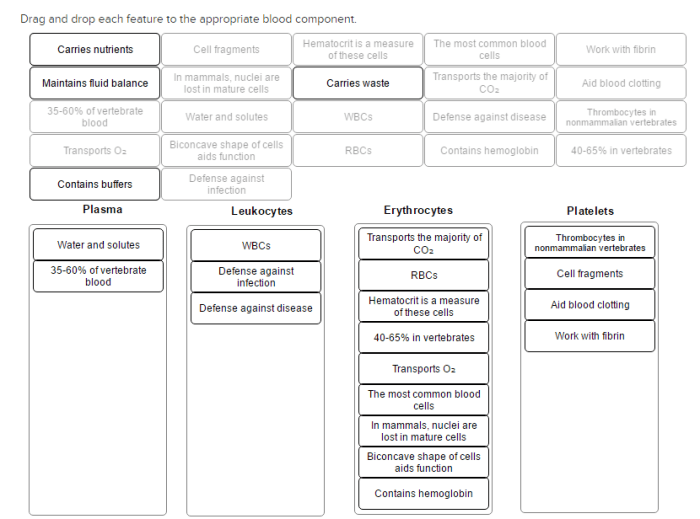
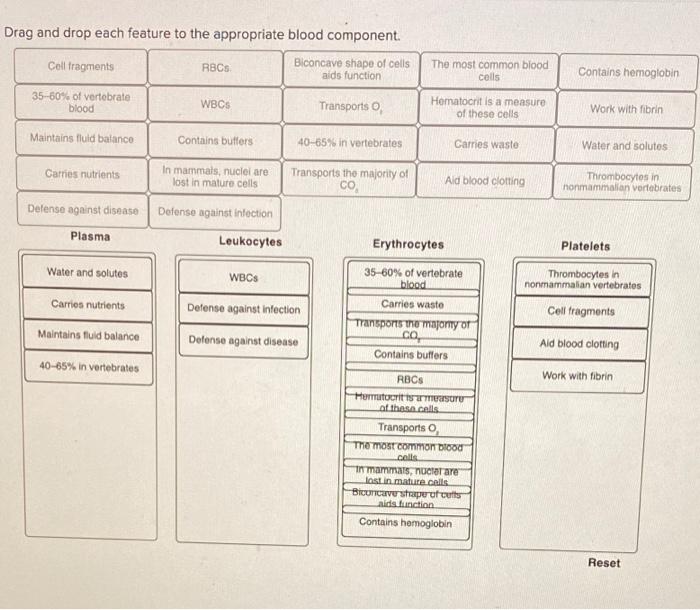
Embark on an interactive journey with “Drag and Drop Each Feature to the Appropriate Blood Component,” where you’ll unravel the intricacies of blood composition through an engaging and immersive experience. This guide empowers you to explore the vital roles of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, providing a comprehensive understanding of their functions and contributions to maintaining optimal health.
Delve into the composition of plasma, the liquid component that transports essential nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body. Discover the remarkable structure and function of red blood cells, responsible for oxygen transport. Unravel the diverse types and functions of white blood cells, the guardians of our immune system.
Finally, explore the intricate role of platelets in blood clotting, ensuring the body’s ability to heal and repair.
Blood Components: Drag And Drop Each Feature To The Appropriate Blood Component
Blood is a complex fluid that consists of several components, each with its unique functions and characteristics. The primary components of blood include plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Plasma, Drag and drop each feature to the appropriate blood component
Plasma is the liquid component of blood that makes up about 55% of its volume. It is composed of water, electrolytes, proteins, hormones, and other molecules.
- Functions of Plasma:
- Transporting nutrients, hormones, and waste products
- Maintaining blood pH and electrolyte balance
- Regulating blood pressure
- Composition of Plasma:
- Water (90-92%)
- Proteins (7-8%): Albumin, globulins, fibrinogen
- Electrolytes (1%): Sodium, potassium, chloride
- Other molecules: Hormones, lipids, waste products
- Role in Blood Clotting:Plasma contains clotting factors that are essential for the formation of blood clots.
Red Blood Cells
Red blood cells are the most abundant cells in blood, accounting for about 45% of its volume. They are responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the tissues.
- Structure of Red Blood Cells:
- Biconcave disks with no nucleus or other organelles
- Filled with hemoglobin, a protein that binds to oxygen
- Function of Hemoglobin:
- Binds to oxygen molecules in the lungs
- Releases oxygen molecules in the tissues
- Role in Oxygen Transport:Red blood cells are responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to all tissues and organs in the body.
White Blood Cells
White blood cells are part of the immune system and are responsible for defending the body against infection and disease.
- Types of White Blood Cells:
- Neutrophils: Most abundant, phagocytic
- Lymphocytes: Include T cells, B cells, and NK cells
- Monocytes: Become macrophages in tissues
- Eosinophils: Involved in allergic reactions
- Basophils: Release histamine in response to allergens
- Functions of White Blood Cells:
- Phagocytosis: Ingesting and destroying foreign particles
- Antibody production: Producing antibodies to neutralize pathogens
- Cell-mediated immunity: Destroying infected cells
- Role in the Immune System:White blood cells are essential for the body’s defense against infection and disease.
Platelets
Platelets are small, disk-shaped cells that play a crucial role in blood clotting.
- Structure of Platelets:
- Small, disk-shaped cells with no nucleus
- Contain granules that store clotting factors
- Function of Platelets:
- Forming platelet plugs to stop bleeding
- Releasing clotting factors to form blood clots
- Role in Blood Clotting:Platelets are essential for the formation of blood clots to prevent excessive bleeding.
Detailed FAQs
What is the primary function of plasma?
Plasma serves as the liquid medium for transporting essential nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body.
How do red blood cells facilitate oxygen transport?
Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, a protein that binds to oxygen molecules, enabling the efficient transport of oxygen to tissues and organs.
What is the role of white blood cells in the immune system?
White blood cells are responsible for recognizing and eliminating pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses, protecting the body from infection.
How do platelets contribute to blood clotting?
Platelets aggregate and form a clot at the site of blood vessel damage, preventing excessive bleeding and promoting healing.